What is Guillain-Barré syndrome?
Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) is a rare neurological disorder that affects the peripheral nervous system. It occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the nerves, leading to muscle weakness and paralysis.

Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) is a rare neurological disorder that affects the peripheral nervous system. It occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the nerves, leading to muscle weakness and paralysis.
GBS is relatively rare. Less than 6,000 people develop GBS each year in the United States
Centers for Disease Control (CDC)There are several types of GBS, each with its own specific characteristics. While the core symptoms of weakness, numbness, and tingling are common across all types, GBS can manifest in different ways depending on which part of the nerve is attacked.
Guillain-Barré syndrome can affect people of all ages, though it’s more common in adults and slightly more prevalent in males. While anyone can be susceptible, those who have recently experienced an infection, such as a respiratory or gastrointestinal illness, may have an increased risk of developing GBS.
The exact cause of Guillain-Barré Syndrome remains unknown, but it is believed to result from an autoimmune response triggered by infections. The immune system mistakenly attacks peripheral nerves, damaging the myelin sheath and disrupting nerve signals, leading to weakness, numbness, and paralysis.
Common triggers include respiratory or gastrointestinal infections caused by certain bacteria or viruses. In rare cases, GBS has been linked to recent vaccinations, including the flu vaccine, although the risk is extremely low.
Risk factors for GBS include:
Having one or more risk factors does not guarantee the development of GBS. If you or a loved one experiences symptoms of GBS, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
If you or a loved one experiences any of these symptoms, seek medical attention immediately. The diagnostic process involves a thorough medical history review, physical examination, and various tests such as:
These tests help healthcare professionals determine the presence of nerve damage and rule out other conditions with similar symptoms. Differential diagnosis is crucial to rule out other conditions such as:
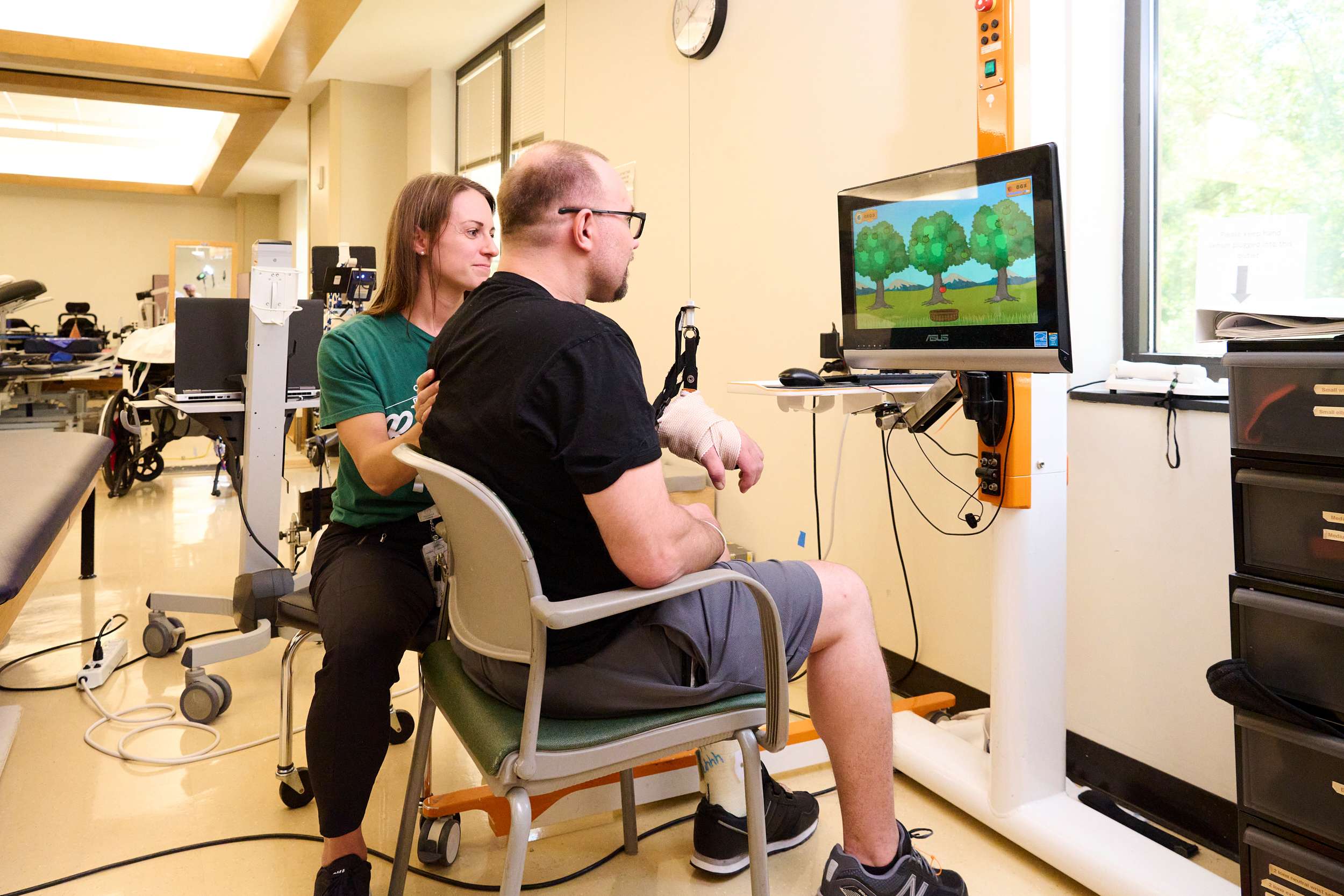
Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) treatment focuses on reducing symptoms, preventing complications, and promoting recovery. Key treatments include intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) to reduce the immune system’s attack on nerves, plasma exchange (plasmapheresis) to remove harmful antibodies, and medications for pain, inflammation, and other symptoms.
Recovery outcomes vary, with some individuals fully recovering and others experiencing lingering symptoms. Rehabilitation through physical, occupational, and speech therapy is crucial for improving strength, coordination, and mobility. Long-term management includes ongoing monitoring and support, with specialized programs available at Shepherd Center to help individuals regain independence.
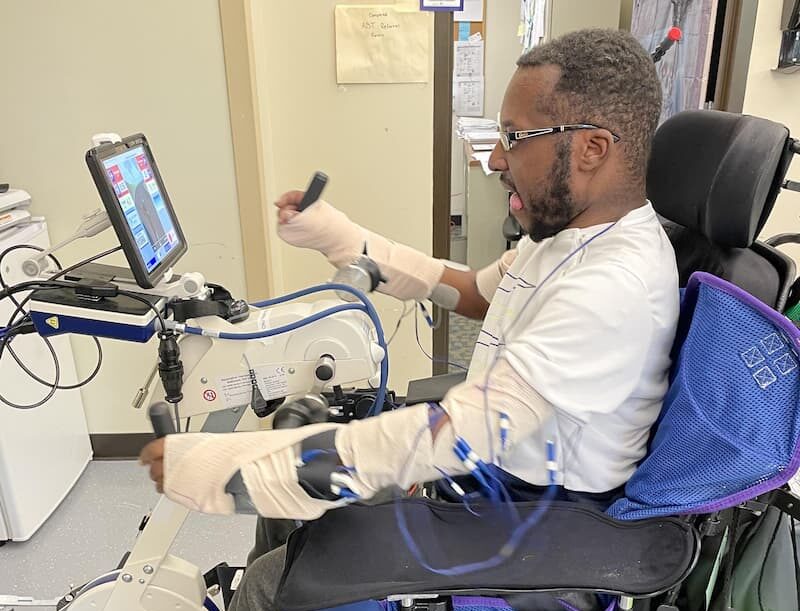
Every individual’s journey is unique, and deciding to pursue rehabilitation can feel overwhelming. That’s why we encourage you to begin with an admissions inquiry.